Crop Production and Management
Exercise:
1). Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
(float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation)
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called crop.
(b) The first step before growing crops is preparation of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would float on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and nutrients and
water from the soil are essential.
2). Match items in column A with those in column B.
A B
(i) Kharif crops (a) Food for cattle
(ii) Rabi crops (b) Urea and super phosphate
(iii) Chemical fertilisers (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and
plant waste
(iv) Organic manure d) Wheat, gram, pea
(e) Paddy and maize
Answers:
(i) Kharif crops → Paddy and maize
(ii) Rabi crops → Wheat, gram, pea
(iii) Chemical fertilisers → Urea and super phosphate
(iv) Organic manure → Animal excreta, cow dung urine and
plant waste
3). Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
Ans: Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton etc.
(b) Rabi crop
Ans: wheat, gram, pea, mustard, linseed etc.
4). Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
Ans: the preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop. One of the most important tas in agriculture is to turn the soil and loosen it. The loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep into the soil. The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing. This is done by using a plough.
(b) Sowing
Ans: Sowing is an important part of crop production. Before sowing, good quality, clean and healthy seeds of good variety are selected. The tool used traditionally for sowing seeds is shaped like a funnel. Nowadays the seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. Sowing by seed drill saves time and labour.
(c) Weeding
Ans: In a field many undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds. The removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light. Thus, they affect the growth of the plant. Farmers adopt many ways to remove weeds and control their growth. Tilling before sowing, uprooting or cutting them close to the ground and controlling weeds using weedicides are some of the methods of controlling weeds.
(d) Threshing
Ans: Harvesting a crop is an important task. In the harvested crop the grain seeds need to be separated from the chaff. This process is called threshing. This is done with the help of a machine called ‘combine’.
5). Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
| Fertilisers | Manures |
| i). Fertiliser is a man-made inorganic salt. | i). Manure is a natural substance. |
| ii). It is prepared in a factory. | ii). It can be prepared in the fields. |
| iii). it does not provide any humus to the soil. | iii) It provides lots of humus to the soil. |
| iv). Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients. | iv). Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
6). What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Ans: The supply of water to crops at regular intervals is called irrigation. The time and frequency of irrigation vary from crop to crop, soil to soil and season to season.
Modern methods of irrigation that help us to conserve water are drip irrigation and sprinkle irrigation.
Drip irrigation: In this system, the water falls drop by drop directly near the roots. So it is called a drip system. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees. Water is not wasted at all.
Sprinkle irrigation: This system is more useful on uneven land where sufficient water is not available. The perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. Water gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining. A sprinkler is useful for lawns, coffee plantation and several other crops.
7). If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Ans: Wheat does not require much water for growth. In the kharif season rains are very frequent. The excess water during rains may cause harm to the wheat crop.
8). Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Ans: Continuous cultivation of crops makes the soil poor in nutrients.
9). What are weeds? How can we control them?
Ans: In a field many undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds. The removal of weeds is called weeding. Tilling before sowing, uprooting or cutting them close to the ground and controlling weeds using weedicides are some of the methods of controlling weeds.
10). Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
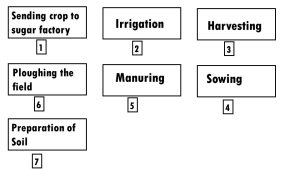
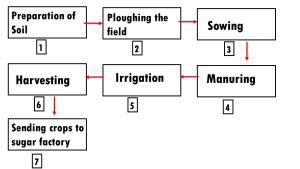
11). Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
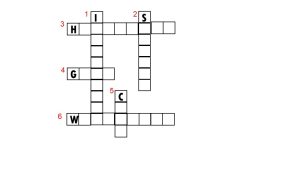
Down
1). Providing water to the crops.
2). Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5). Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3). A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4). A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6). A process of separating the grain from chaff.

Additional Questions.
Fill in the blanks.
i). The loose soil allows the root to breathe easily.
ii). Ploughs are made up of wood or iron.
iii). Big clumps of soil present in the loosed soil are called crumbs.
iv). Manure is an organic substance obtained from the decomposition of plants or animal waste.
v). Water is absorbed by the plant roots.
vi). The undesirable plants are called weeds.
Write whether True or False.
i). Gram is a Rabi crop.
Ans: True.
ii). Wheat is a Kharif crop.
Ans: False
iii). Cultivation of crops involves several activities.
Ans: True
iv). The use of cultivator saves labour and time.
Ans: True
v). Damaged seeds sink in the water.
Ans: False
vi). Seed drill sows the seeds uniformly at equal distance and depth.
Ans: True
vii). Continuous cultivation of crops makes the soil poor in nutrients.
Ans: True
viii). The time and frequency of irrigation varies from season to season.
Ans: True
Answer in one sentence.
1). What do you mean by crop?
Ans: The plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop.
2). What are Kharif crops?
Ans: The crops that are sown in the rainy season are called Kharif crops.
3). What are Rabi crops?
Ans: The crops that are sown in the winter season are called Rabi crops.
4). What is tilling of the land?
Ans: The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling of the land.
5). What is plough?
Ans: The device is used for ploughing is plough.
6). Name the tools used in agriculture.
Ans: The tools used in agriculture are plough, hoe, cultivator, khupri, sickle, filler etc.
7). What is an irrigation?
Ans: The supply of water to crops at regular intervals of time is called irrigation.
8). Name some of the sources of water for irrigation.
Ans: The sources of water for irrigation are – wells, tubewells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals.
9). What is weeding?
Ans: The removal of the weeds is called as weeding.
10). What are weedicides?
Ans: The chemicals that are used for removal of weeds are called weedicides.
11). What is harvesting?
Ans: The cutting of crop after maturation is harvesting.
12). What is threshing?
Ans: The separation of the grains from the chaff is threshing.
13). Name some harvest festivals.
Ans: Pongal, Baisakhi, Nabanya and Bihu.
14). Name devices used for storage of grains.
Ans: i). Silos and ii) Granaries
Answer in short.
1). List some of the activities involved in agriculture.
Ans: Activities involved in agriculture are as follows.
(i) Preparation of soil
(ii) Sowing
(iii) Adding manure and fertilisers
(iv) Irrigation
(v) Protecting from weeds
(vi) Harvesting
(vii) Storage
2). Write two disadvantages in using fertilisers.
Ans: The two disadvantages in using fertilisers are as follows.
i). Excessive use of fertilisers makes the soil less fertile.
ii). Fertilisers have also become a source of water pollution.
3). Write the advantages of using of manure in agriculture.
Ans: The advantages of using manures in agriculture are as follows.
i). Manures improves soil texture.
ii). It enhances the water retaining capacity of soil.
iii). It replenishes the soil with the nutrients.
4). Write in short about crop rotation.
Ans: The process of growing different crops alternately year after year is called crop rotation. This helps in the replenishment of the soil with nitrogen and increases the fertility of the soil.
Give reasons.
i) Soil is loosed before the seeds are sown.
Ans: Loosening of the soil allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. The loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep into the soil. It allows the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil that further turns the soil and make it loose and add humus to it. Therefore, soil is loosed before the seeds are sown.
ii). weeding is necessary.
Ans: Weeding is necessary as they compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light. They interfere in harvesting and may be poisonous for animals and human beings. Therefore, weeding is necessary.
![]()
