Electric Current and Its Effects
Exercise
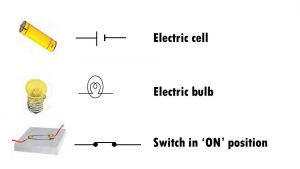
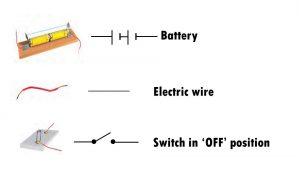
1). Draw in your notebook the symbols to represent the following components of electrical circuits: connecting wires, switches in the ‘OFF’ position, bulb, cell, switch in the ‘ON’ position and battery.
Ans:
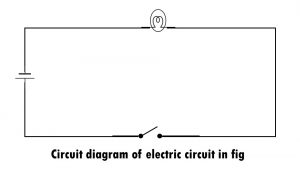
2). Draw the circuit diagram to represent the circuit shown in fig.

Ans:
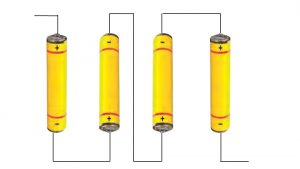
3). Fig 14.22 shows four cells fixed on a board. Draw lines to indicate how you will connect their terminals with wires to make a battery of four cells.

Ans:
4). The bulb in the circuit shown in Fig.14.23 does not glow. Can you identify the problem? Make necessary changes in the circuit to make the bulb glow.
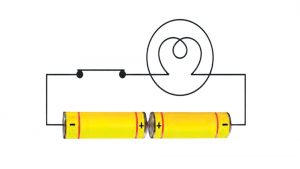
Ans: The problem in the circuit is in the connection of two cells. Here both the positive terminals are connected to each other. To make the bulb glow positive terminal of one cell should be connected to the negative terminal of the other cell.
5). Name any two effects of electric current.
Ans: The two effects of elcectric current are heating effect and magnetic effect.
6). When the current is switched on through a wire, a compass needle kept nearby gets deflected from its north-south position. Explain.
Ans: When electric current passes through a wire, it behaves like a magnet. The needle of compass is a tiny magnet, which points in north-south direction. Therefore as soon as we bring a compass needle near an electric current it gets delfected.
7). Will the compass needle show deflection when the switch in the circuit shown by Fig.14.24 is closed?
Ans: No. because there is no cell connected in the circuit.
8). Fill in the blanks:
(a) Longer line in the symbol for a cell represents its positive terminal.
(b) The combination of two or more cells is called a battery.
(c) When current is switched ‘on’ in a room heater, it becomes red hot.
(d) The safety device based on the heating effect of electric current is called a fuse.
9). Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(a) To make a battery of two cells, the negative terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the other cell. (T/F)
Ans: F
(b) When the electric current through the fuse exceeds a certain limit, the fuse wire melts and breaks. (T/F)
Ans: T
(c) An electromagnet does not attract a piece of iron. (T/F)
Ans: F
(d) An electric bell has an electromagnet. (T/F)
Ans: T
10). Do you think an electromagnet can be used for separating plastic bags from a garbage heap? Explain.
Ans: Electromagnet develops a magnetic property and it will attract only magnetic substances. Since plastic is a non-magnetic substance it cannot be used for separating plastic bags from a garbage heap.
11). An electrician is carrying out some repairs in your house. He wants to replace a fuse by a piece of wire. Would you agree? Give reasons for your response.
Ans: No. Electric fuse is made from special materials that melt quickly when large electric currents are passed through them. An ordinary wire may not perform this function and it can damage the electric appliances and also cause fire.
12). Zubeda made an electric circuit using a cell holder shown in Fig. 14.4, a switch and a bulb. When she put the switch in the ‘ON’ position, the bulb did not glow. Help Zubeda in identifying the possible defects in the circuit.
Ans: The possible defects are as follows.
(i) The cell may not be connected in proper way. Electric current pass only when opposite terminals are connected to each other.
(ii) Check the connections
(iii) Check the condition of the bulb and replace it if it is fused.
13). In the circuit shown in Fig. 14.25 Fig. 14.25
(i) Would any of the bulb glow when the switch is in the ‘OFF’ position?
Ans: No. none of the bulb glow unless the switch is in ‘ON’ position.
(ii) What will be the order in which the bulbs A, B and C will glow when the switch is moved to the ‘ON’ position?
Ans: All the three bulbs will glow at the same time.
Additional Questions
Fill in the blanks.
i) The wires used to connect the various components in a circuit are represented by lines.
ii) We generally represent an electric circuit by its circuit diagram.
iii) The wire gets hot when an electric current passes through it.
iv). The coil of wire in an electric heater is called as element.
v). When an electric current flows through a wire, it behaves like a magnet.
True or False
i). In the symbol of the electric cell, the longer line represents the positive terminal and the thicker, shorter line represents the negative terminal.
Ans: True
ii). When electric current passes through a wire, it behaves like a magnet.
True.
iii). When the switch is in the ‘OFF’ position the circuit is complete.
Ans: False.
iv). When the switch is in the ‘OFF’ position the circuit is open.
Ans: True.
v). When the switch is in the ‘ON’ position the circuit is complete.
Ans: True.
vi). When the switch is in the ‘ON’ position the circuit is closed.
Ans: True.
vii). LED bulbs consume less electricity as compared florescent tubes or CFLs.
Ans: True.
Answer the following questions.
1). What is meant by battery.
Ans: Combination of two or more cells joined together is known as battery.
2). What is filament?
Ans: The thin wire in the electric bulb is called filament.
3). Name two appliances that use of heating effect of electric current?
Ans: Electric heater and electric iron.
4). Name the two devices that protect the electric appliances in our home from damage when current exceeds the safe limitedly.
Ans: Electric fuse and MCBs.
5). Who discovered the magnetic effect of electric current?
Ans: Hans Christian Oersted.
6). Name devices based on the magnetic effect of electric current?
Ans: Crane, electric bell, loud speakers, telephone etc.
7). What are electromagnets?
Ans: When an electric current is passed through a coil of wire, it behaves like a permanent magnet.
8). Name two applications of electromagnets.
Ans: Electric bell and crane.
Click here for the solutions of
6). Physical and Chemical Changes
7). Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
8). Winds, Storms and Cyclones
11). Transportation in Animals and Plants
14). Electric Currents and its Effects
16). Water: A Precious Resource
![]()

